Vegetation diversity protects against childhood asthma: results from a large New Zealand birth cohort
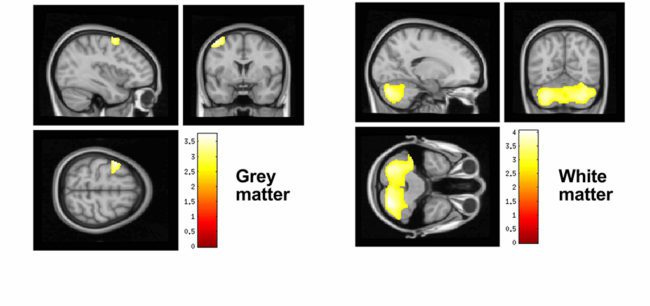
Researchers assessed the association between the natural environment and asthma in 49,956 New Zealand children born in 1998 and followed up until 2016 using routinely collected data. Children who lived in greener areas, as measured by the normalized difference vegetation index, were less likely to be asthmatic.